FIGURE 2
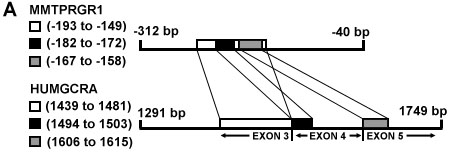
(a) A schematic of local nucleotide sequence alignments for exon 3:
1318 to 1485 bp, exon 4: 1486 to 1602 bp and exon 5: 1603 to 1626 bp of the GR
DBD (GENBANK locus HUMGCRA) vs mouse mammary tumor virus 5' long
terminal repeat (GENBANK locus MMTPRGR1) nucleotides ranging from -312 to
-40 upstream from the MMTV transcription start site.
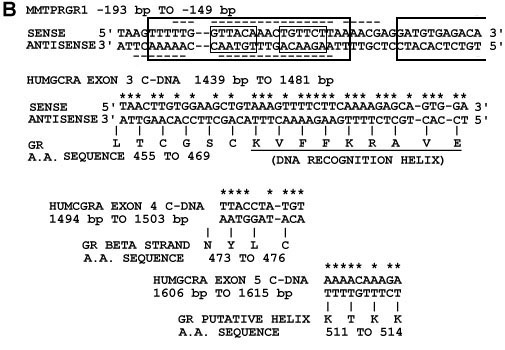
(b) Nucleotide sequence alignments from figure 2a. Above is shown the MMTPRGR1 nucleotide sequence
within which GR binding sites have been detected with nuclease footprinting
studies by others and are shown as large boxes (12) and
dashed underlines and overlines (13-14). Small boxes
contain the two glucocorticoid receptor binding half-sites GTTACA and TGTTCT
respectively. Nuclecotide base pair matches are starred. Below the HUMGCRA cDNA
sequences are shown their corresponding amino acid sequences in Dayhoff
(8) one-letter code with the amino acids numbered
as in the Rat GR (1). The recognition helix in the exon 3 alignment is underlined.
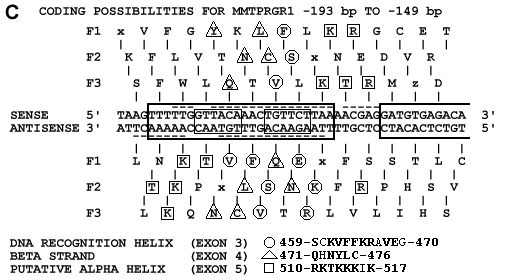
(c) The nucleotide sequence of MMTPRGR1 showing maximum subsequence
similarity (see 2b) is translated to amino acids (in Dayhoff one-letter code) in all
reading frames (F1, F2, and F3), on both strands: top (rightward: sense 5'-3') and
bottom (leftward: antisense 5'-3'). Circles, triangles and squares indicate codons in
the DNA sequence with which cognate amino acids from the GR DBD are aligned.
Circles = codons for exon 3 encoded DNA recognition helix amino acids, triangles
= codons for exon 4 encoded beta strand amino acids and squares = codons for
exon 5 encoded putative alpha helix amino acids. The amino acid sequences of
these structures are shown at the bottom of the figure. Amino acids aligned with
cognate codons are in boldface type.

(a) A schematic of local nucleotide sequence alignments for exon 3:
1318 to 1485 bp, exon 4: 1486 to 1602 bp and exon 5: 1603 to 1626 bp of the GR
DBD (GENBANK locus HUMGCRA) vs mouse mammary tumor virus 5' long
terminal repeat (GENBANK locus MMTPRGR1) nucleotides ranging from -312 to
-40 upstream from the MMTV transcription start site.

(b) Nucleotide sequence alignments from figure 2a. Above is shown the MMTPRGR1 nucleotide sequence
within which GR binding sites have been detected with nuclease footprinting
studies by others and are shown as large boxes (12) and
dashed underlines and overlines (13-14). Small boxes
contain the two glucocorticoid receptor binding half-sites GTTACA and TGTTCT
respectively. Nuclecotide base pair matches are starred. Below the HUMGCRA cDNA
sequences are shown their corresponding amino acid sequences in Dayhoff
(8) one-letter code with the amino acids numbered
as in the Rat GR (1). The recognition helix in the exon 3 alignment is underlined.

(c) The nucleotide sequence of MMTPRGR1 showing maximum subsequence
similarity (see 2b) is translated to amino acids (in Dayhoff one-letter code) in all
reading frames (F1, F2, and F3), on both strands: top (rightward: sense 5'-3') and
bottom (leftward: antisense 5'-3'). Circles, triangles and squares indicate codons in
the DNA sequence with which cognate amino acids from the GR DBD are aligned.
Circles = codons for exon 3 encoded DNA recognition helix amino acids, triangles
= codons for exon 4 encoded beta strand amino acids and squares = codons for
exon 5 encoded putative alpha helix amino acids. The amino acid sequences of
these structures are shown at the bottom of the figure. Amino acids aligned with
cognate codons are in boldface type.