Molecular Dynamics Simulations - Figure 2.
FIGURE 2
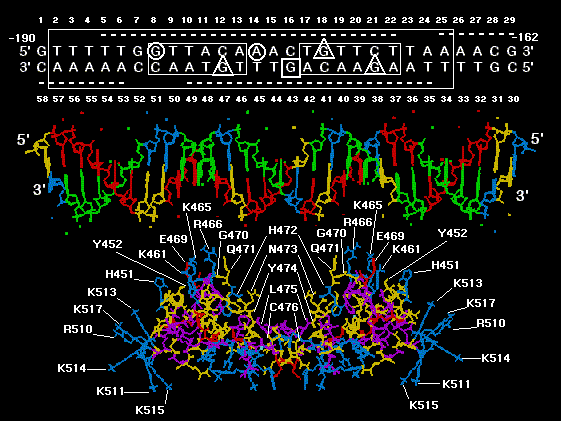
A computer model of NMR GR DBD dimer in complex with the 29 bp nucleotide
sequence of MMTV GRE from GENBANK locus MMTPRGR1. The protein is docked at a
distance of about 10 angstroms from the DNA for visual clarity. The GR DBD amino acids are
color coded based on side chain polarity: positively charged side chains = blue, negatively
charged side chains = red, uncharged polar side chains = yellow, and nonpolar side chains =
purple. Amino acids of the GR DBD which are oriented toward the GRE are labelled using the
Dayhoff one letter code and are numbered as in the rat GR. The following amino acids are labeled:
Exon 3 encoded amino acids of the first "zinc finger", H 451 and Y 452, exon 3 encoded DNA
recognition helix amino acids, K 461, K 465, R 466, E 469, and G 470, exon 4 encoded beta
strand amino acids, Q 471, H 472, N 473, Y 474, L 475, and C 476 and finally, exon 5 encoded
predicted alpha helix amino acids, R 510, K 511, K 513, K 514, K 515, and K 517. The DNA
nucleotides are assigned the following colors: A = green, T = red, G = yellow and C = blue. The
nucleotide sequence of the DNA model was derived from a GRE within GeneBank locus
MMTPRGR1 which shared maximal nucleotide subsequence similarity with subsequences within
the GR cDNA encoding the DNA recognition helix in exon 3, a beta strand in exon 4 and a
predicted alpha helix in exon 5 (11). Above the DNA model is a schematic of the MMTPRGR1
GRE and flanking regions, numbered above and below with the 5' sense strand read left to right,
starting at -190 upstream from the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) transcription start site
and ending at -162 = 1 to 29. The antisense strand reads right to left from -162 to -190 = 30 to 58.
boxes and underlines/overlines are as in figure1b . Methylation inhibition studies by others (19)
are summarized with the following symbols: Triangles show nucleotides where methylation
inhibits receptor binding. The circles show nucleotides which, when methylated, do not inhibit
receptor binding but cannot be methylated after receptor is bound. The square shows a guanine
that is hypermethylated in the presence of bound receptor. The GR/GRE model shown is to be
used as a key for locating interactions from molecular dynamics found between the GR DBD
amino acids and nucleotides of the GRE and its flanks (see tables 1 and 2). The color coding and
numbering scheme in this figure is used in all subsequent molecular models.


